📖 Table of Content:
- 1. Playfulness
- 2. Teething
- 3. Overstimulation
- 4. Fear or Anxiety
- 5. Defensive Posture
- 6. Pain or Discomfort
- 7. Territorial Behavior
- 8. Redirected Aggression
- 9. Lack of Socialization
- 10. Hunting Instincts
- 11. Boredom
- 12. Habit
- 13. Miscommunication
- 14. Attention Seeking
- 15. Frustration
- 16. Medical Issues
- 17. Affection
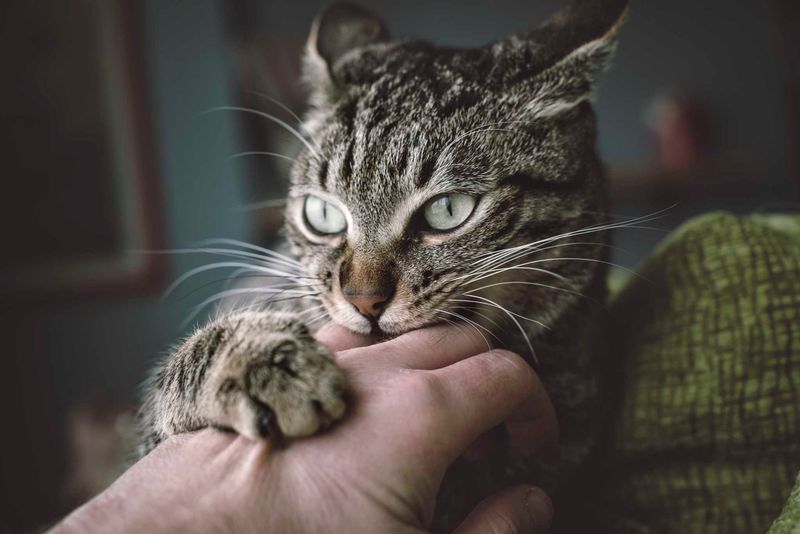
Cats may bite for numerous reasons, and understanding these behaviors can help prevent misunderstandings. Whether it’s due to playfulness, discomfort, or territorial instincts, each bite serves as a form of communication. Recognizing the underlying causes can offer insight into how to approach and manage the behavior appropriately.
The nature of a cat’s bite can vary greatly depending on the situation. Some bites are playful and lighthearted, while others are more defensive or even aggressive. Knowing when a cat is playing versus when it’s feeling threatened is essential for fostering a safe and harmonious relationship.
Addressing cat bites requires patience and awareness of their body language. By observing their reactions, it becomes easier to differentiate between a friendly nip and a warning sign. Understanding why cats bite is key to improving interactions and ensuring a positive bond with your feline companion.
1. Playfulness
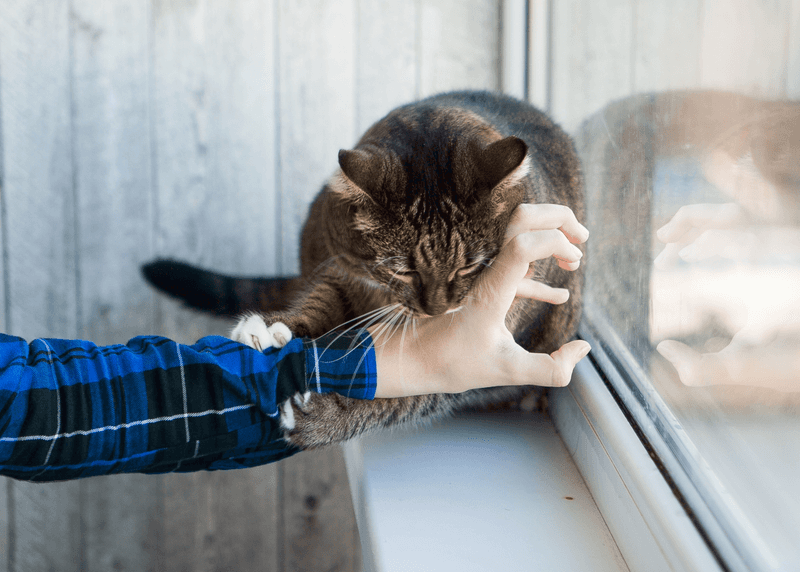
Cats often bite during play as a part of their natural instinct. When kittens play with each other, they use their mouths. Even as adults, this trait can persist. It’s vital to distinguish playful biting from aggression. A playful cat has relaxed body language, and its bites are gentle.
Providing toys and interactive play sessions can help redirect this behavior. For a more enjoyable playtime, focus on toys that mimic prey, like feather wands or small balls. Establish boundaries by stopping play if the biting becomes too hard.
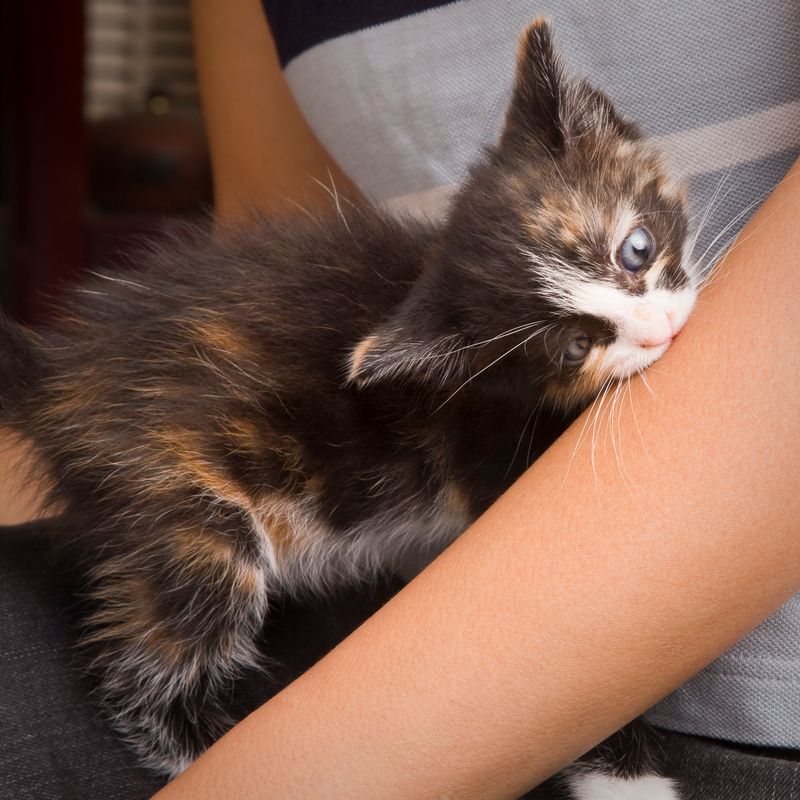
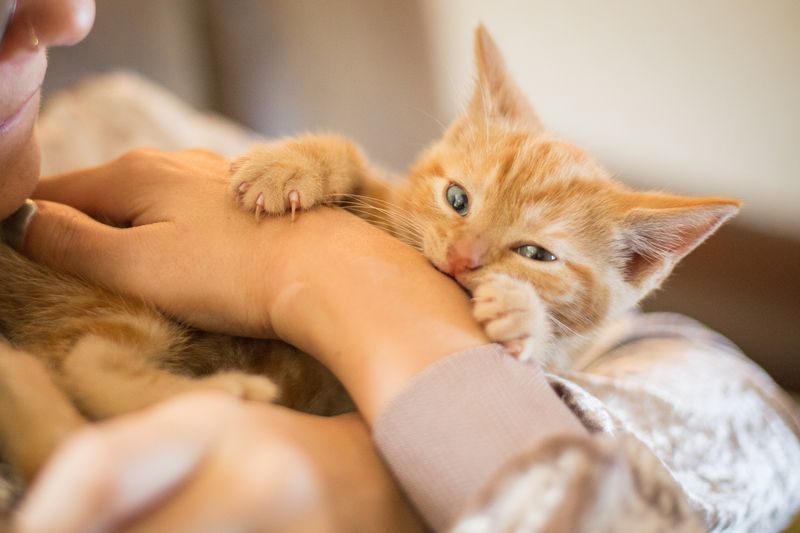
2. Teething
Teething is a common phase where kittens might bite more than usual. As their new teeth grow, they experience discomfort. This discomfort can lead to increased biting as they seek relief. Providing appropriate chew toys can soothe their gums.
Ensure these toys are specifically designed for teething kittens to prevent damage to their developing teeth. This stage is temporary but crucial for their dental health. Maintaining patience and offering suitable options will ease their discomfort and protect your fingers from being a target.
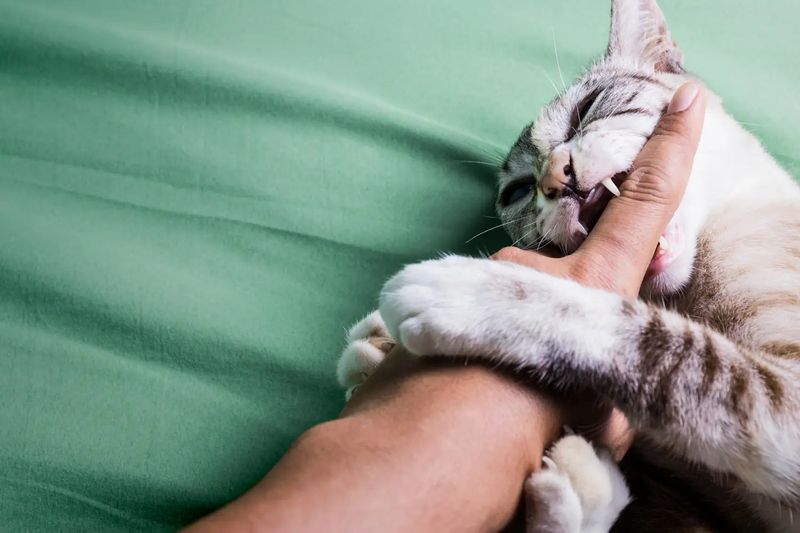
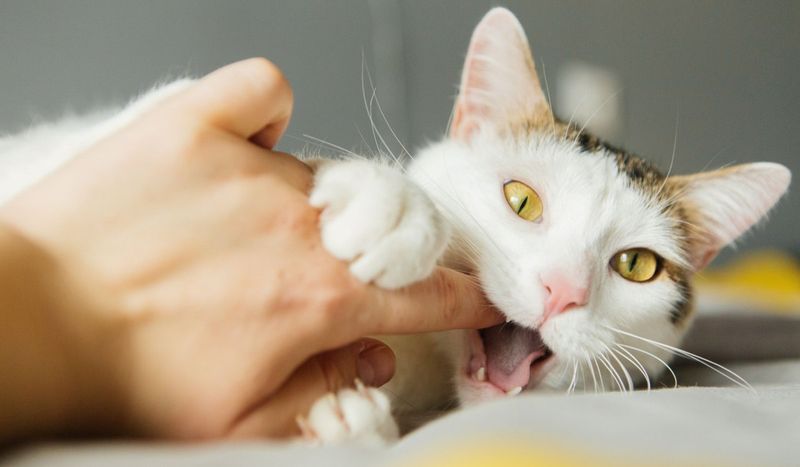
3. Overstimulation
Some cats bite due to overstimulation, especially when being petted for too long. Initially, they may enjoy the affection, but it can quickly turn overwhelming. Signs of overstimulation include twitching tails or ears, and sudden biting. Recognizing these signs can prevent bites.
Each cat’s tolerance varies, so observing their body language is essential. Interrupting petting sessions before the cat becomes overstimulated fosters a positive bond. Offering breaks ensures that affection remains enjoyable for both you and your feline friend.
4. Fear or Anxiety
Defensive biting is a common response when a cat is scared or anxious. If a cat perceives a threat, it may use biting as a way to protect itself. Identifying triggers, such as changes in the environment or loud noises, can help manage this behavior.
Creating a safe and comforting space for your cat is crucial. Gradual exposure to the fear source can assist in reducing anxiety. Clear signs of fear include dilated pupils and flattened ears. Addressing the root cause with patience can build trust, reducing the likelihood of fear-induced bites.
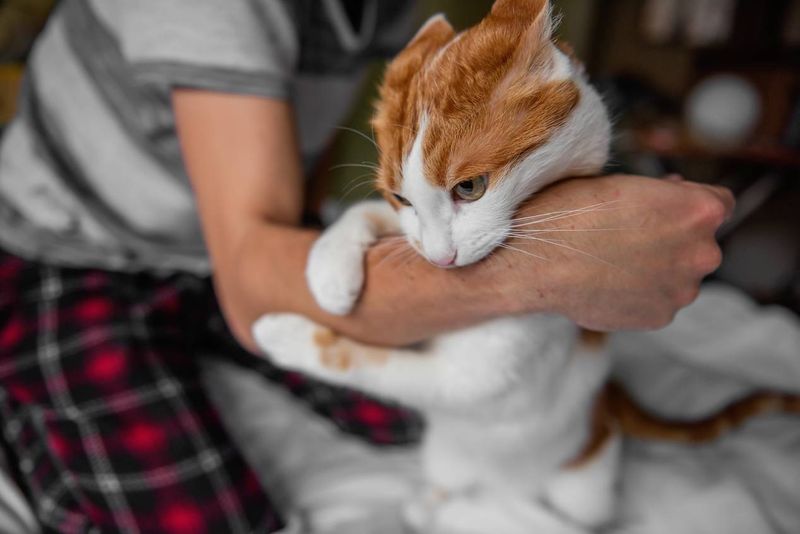
5. Defensive Posture
When a cat feels trapped, it may bite as a defense mechanism to protect itself. This is an instinctual behavior triggered by fear. Recognizing defensive signals such as hissing or fluffed-up fur, and moving slowly, can help prevent the cat from becoming more aggressive.
Giving them space reassures the cat, showing you respect their boundaries. Over time, this approach can help reduce defensive biting. Building trust involves understanding and patience, enhancing the cat’s sense of security. A secure cat is less likely to bite defensively.
6. Pain or Discomfort
Unexpected biting can be a cat’s way of responding to pain or discomfort. If a cat feels pain when touched in a certain area, it may react defensively by biting. Regular vet visits and observing changes in movement or behavior can help identify any health problems, preventing future biting incidents.
Providing a comfortable and pain-free environment is key. Understanding and empathy towards a cat’s physical state foster a deeper connection and minimize pain-related biting.
7. Territorial Behavior
Cats can exhibit territorial behavior, which includes biting. They might see intruders as threats to their territory. This behavior is more common in multi-cat households. Identifying and respecting territorial boundaries helps mitigate conflicts. Providing separate spaces for each cat ensures harmony. Gradual introductions to new pets or environments can reduce territorial aggression.
Observing and respecting a cat’s space is vital for peaceful coexistence. Enhancing their environment with perches or hideaways offers comfort, allowing them to feel secure and less prone to territorial biting.
8. Redirected Aggression
When a cat is frustrated by something it can’t reach, redirected aggression can occur, leading to biting nearby individuals. Common triggers include sights or sounds of other animals outside, which the cat may not be able to approach.
Providing distraction with toys or blocking the view can help. Understanding these triggers fosters a calmer environment. Reducing stressors diminishes the likelihood of redirected biting. Engaging your cat in play can redirect their focus, promoting a more peaceful interaction with people and pets.
9. Lack of Socialization
Cats not properly socialized may bite out of fear or uncertainty. Early experiences shape their interactions with humans. Gradual exposure to positive human contact builds trust. Respecting their pace prevents stress.
For older cats, patience and gentle handling are essential. Offering treats and praise for calm behavior reinforces positive associations. Socialization is a continuous process, enhancing their comfort and reducing fear-induced bites. Providing a calm and supportive environment allows them to adjust, fostering a more confident and less fearful feline.
10. Hunting Instincts
Biting is a part of a cat’s natural hunting behavior, driven by their instinct to hunt and capture prey. Interactive toys that mimic the movement of prey provide an outlet for this need. Regular playtime helps redirect this behavior into a positive and stimulating activity.
Encouraging these instincts through structured play prevents them from being directed at humans. Varying play activities keep them engaged and fulfilled. Acknowledging their predatory nature and providing outlets ensures a balanced and happy cat. A well-exercised cat is less likely to bite out of boredom or frustration.
11. Boredom
When cats feel bored, they may bite as a way to entertain themselves or grab attention. A lack of stimulation often leads to these behaviors. Keeping the environment rich with engaging toys and rotating them frequently can help curb biting due to boredom.
Engaging in daily play sessions strengthens your bond and reduces boredom-related biting. Offering new experiences and challenges keeps their mind active. Creating an enriching environment fosters a content and less aggressive cat. A fulfilled cat is more relaxed and less inclined to use biting as a diversion.
12. Habit
Sometimes cats bite out of habit, a behavior reinforced over time. It’s crucial to break this cycle with a consistent response. Avoid rewarding biting with attention, even negative. Redirecting to suitable toys helps alter the habit.
Consistency in response teaches boundaries. Patience and alternative activities play a key role in modification. Reinforcing positive behavior with treats or praise encourages change. Over time, this approach diminishes habitual biting, fostering a more harmonious relationship. A consistent and understanding approach leads to a well-adjusted and less bite-prone cat.
13. Miscommunication
When humans fail to understand a cat’s body language, bites may occur as a form of communication. Cats use subtle movements and gestures to express their feelings, which can easily be misinterpreted. By paying attention to their reactions to touch, owners can foster a better understanding and prevent accidental bites.
Adjusting your approach based on their feedback strengthens your bond. Clear communication through attentive observation reduces accidental bites. Respecting their signals nurtures a trusting relationship. A strong awareness of their language minimizes misunderstanding, leading to a more satisfying companionship. A well-understood cat is more comfortable and less likely to bite.
14. Attention Seeking
Biting as a way to get attention can become a recurring behavior if it results in interaction. Redirecting the cat’s focus to alternative, non-biting behaviors reinforces positive attention-seeking methods. Recognizing and rewarding the right behaviors promotes healthier communication with your cat.
Ignoring unwanted biting while rewarding gentle interactions cultivates a positive dynamic. Engaging your cat in play or petting sessions when calm ensures healthy attention-seeking habits. This approach fosters a more balanced relationship, reducing attention-driven biting incidents. A loving and consistent environment encourages desirable attention-seeking behaviors.
15. Frustration
If a cat’s natural instincts or needs are ignored, biting can become a form of expression. Whether due to boredom, lack of play, or social isolation, these triggers can lead to frustration. Providing a more stimulating environment can alleviate this and prevent the bite.
Understanding their needs reduces frustration-related biting. Offering a variety of outlets for energy ensures a more contented cat. Addressing their emotional state with empathy builds a stronger bond. Acknowledging their frustrations and providing solutions minimizes the chance of biting due to this emotional state.
16. Medical Issues
Underlying medical issues can cause unexpected biting in cats. Health problems might make them more irritable or sensitive. Regular veterinary check-ups ensure early detection and treatment of health concerns. Observing changes in behavior or appetite informs necessary actions.
Addressing medical issues promptly reduces pain-induced biting. Keeping a health journal aids in tracking symptoms. Prioritizing their health fosters a comfortable and happy cat. A well-maintained medical routine ensures a healthy pet, reducing instances of biting due to discomfort or illness. Monitoring their health promotes a peaceful coexistence.
17. Affection
Some cats bite gently as a form of affection, often referred to as “love bites.” This behavior is usually gentle and not aggressive. Understanding the context and body language distinguishes these from other bites. Responding with gentle petting reinforces the positive interaction.
Recognizing affectionate biting fosters a better understanding of your cat’s ways of expressing love. These nips are part of their communication style. Building a strong relationship involves appreciating all their gestures. Embracing their unique methods of showing affection strengthens your bond, making these bites a cherished expression of love.