📖 Table of Content:
- 1. Genetic Basis of Coat Patterns
- 2. Agouti Gene
- 3. Solid Color Gene
- 4. Ticked Pattern
- 5. Embryonic Development
- 6. Temperature Sensitivity
- 7. Temperature Effects
- 8. Wild Ancestors
- 9. Breed Development
- 10. Dilute Gene
- 11. White Spotting
- 12. Classic Tabby
- 13. Mackerel Tabby
- 14. Spotted Tabby
- 15. Ticked Tabby
- 16. Solid or Self-Color
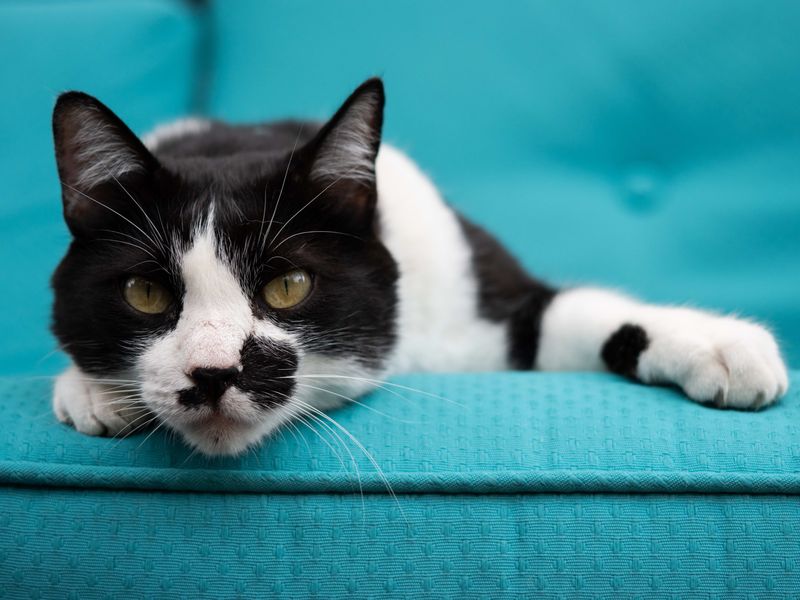
- 17. Bicolor
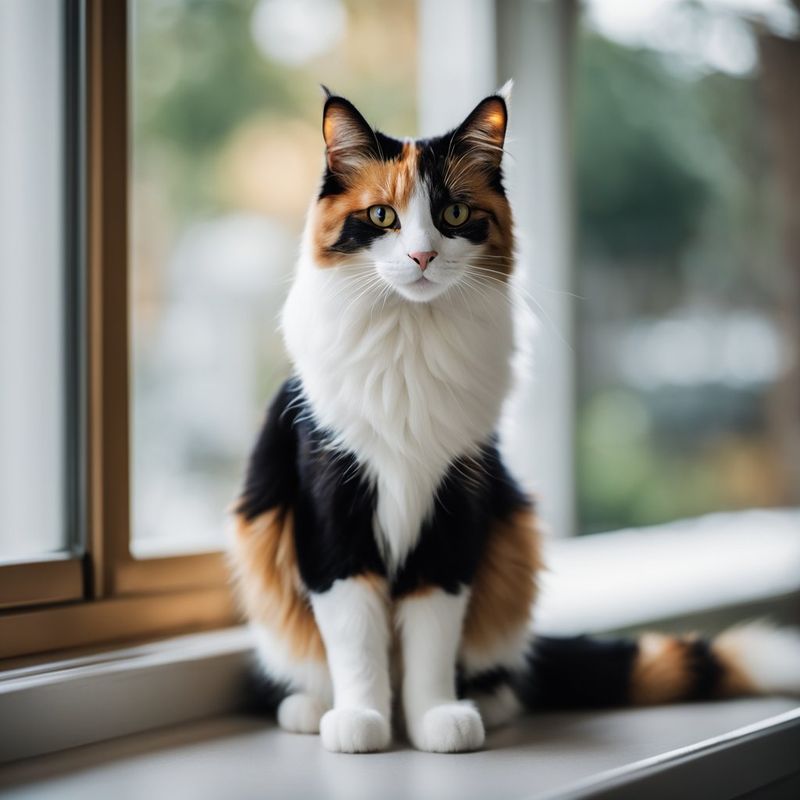
- 18. Calico
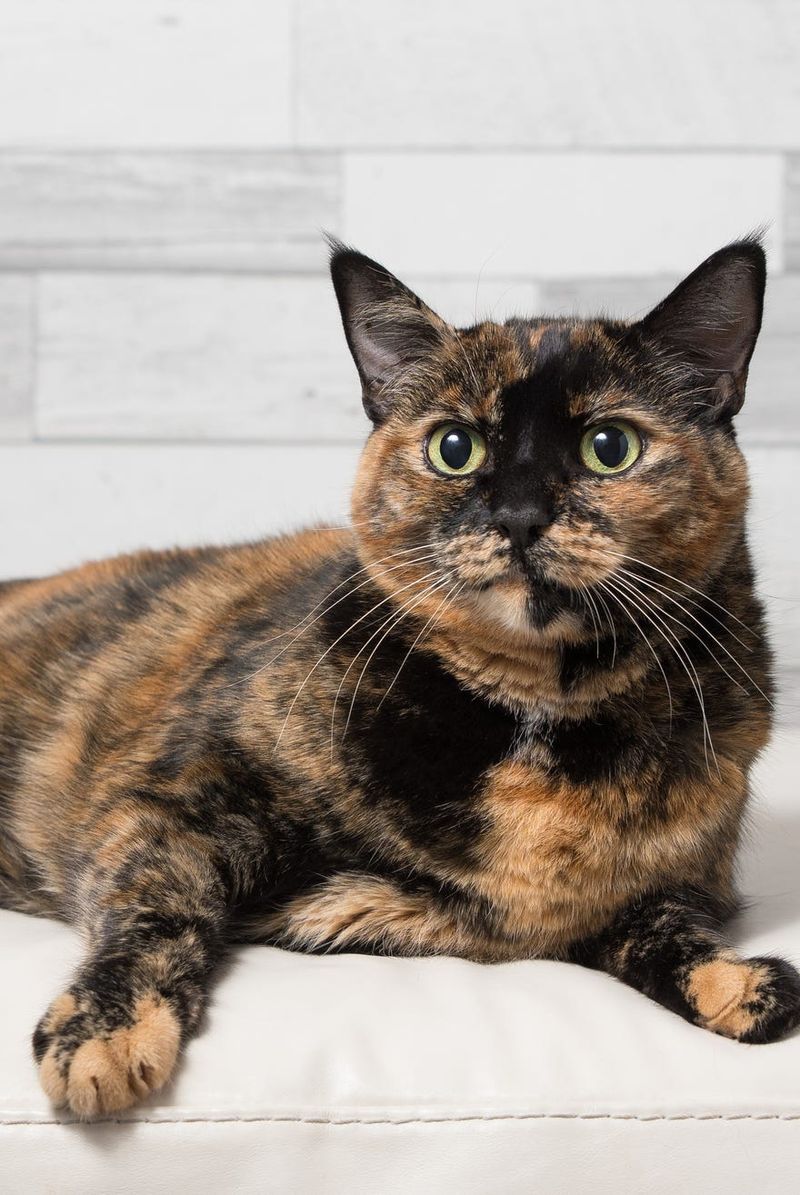
- 19. Tortoiseshell
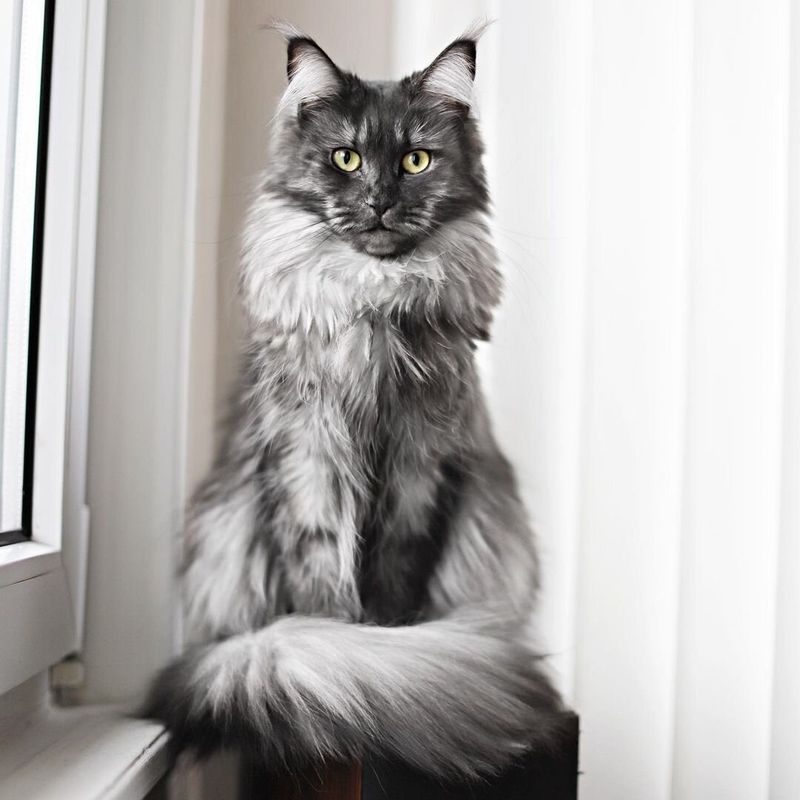
- 20. Smoke
The evolution of coat colors and patterns in domestic cats is a complex interplay of genetics, development, and environmental factors. Over time, these elements have combined to produce the diverse array of feline fur patterns observed today.
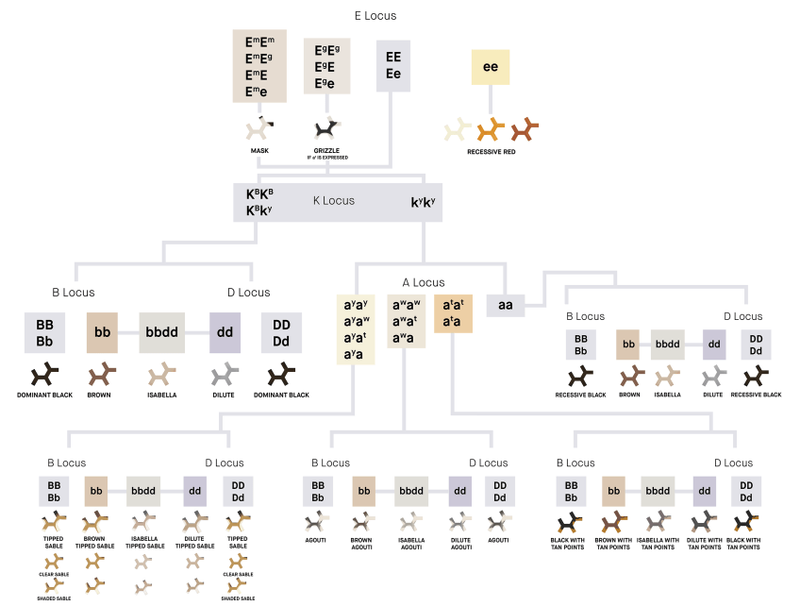
1. Genetic Basis of Coat Patterns
Genetic diversity plays a crucial role in the colorful tapestry of cat fur. The Agouti gene influences patterns like tabby stripes and spots, while the Solid Color gene contributes to uniform coat colors or patterns like white patches. These genes work in tandem to create the stunning variety of feline fur we admire today.
2. Agouti Gene
The Agouti gene, with its remarkable ability to determine pigment distribution, is a key player in creating tabby patterns. It orchestrates the lighter and darker bands in fur, resulting in the classic striped appearance. This gene’s magic allows cats to blend seamlessly into their environments, aiding in their stealth and survival.
3. Solid Color Gene
The Solid Color gene simplifies the canvas, removing patterns to leave behind a sleek, uniform appearance. This genetic trait is responsible for the solid black, white, and other single-colored cats we see. Despite the simplicity, it adds an air of elegance and mystery to our feline companions, enhancing their allure.
4. Ticked Pattern
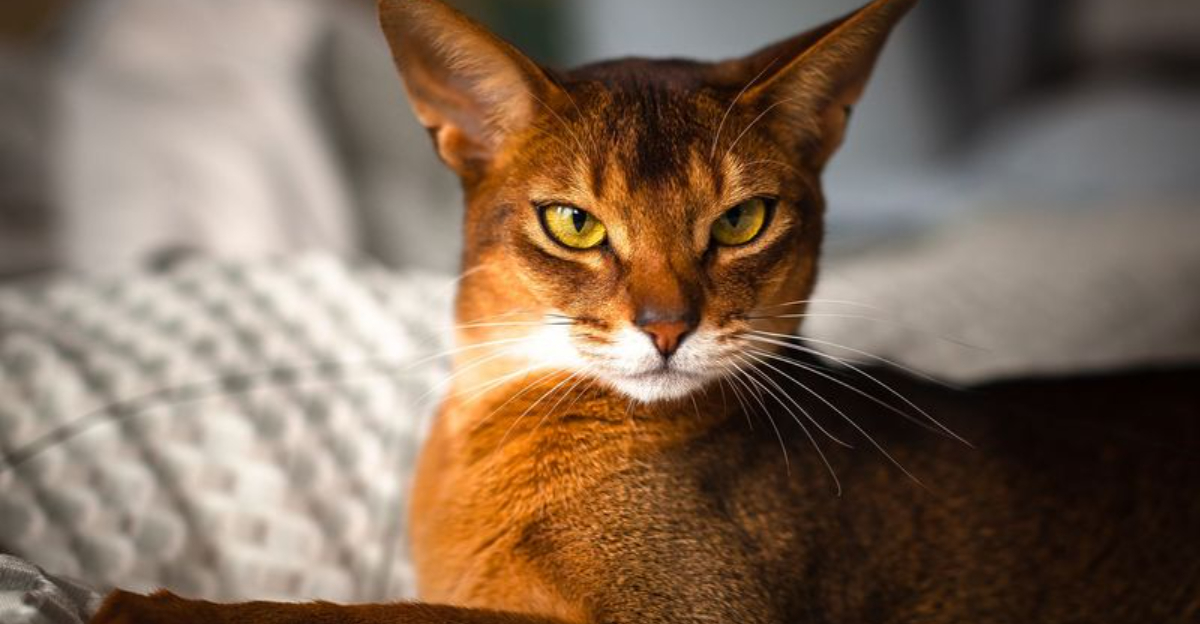
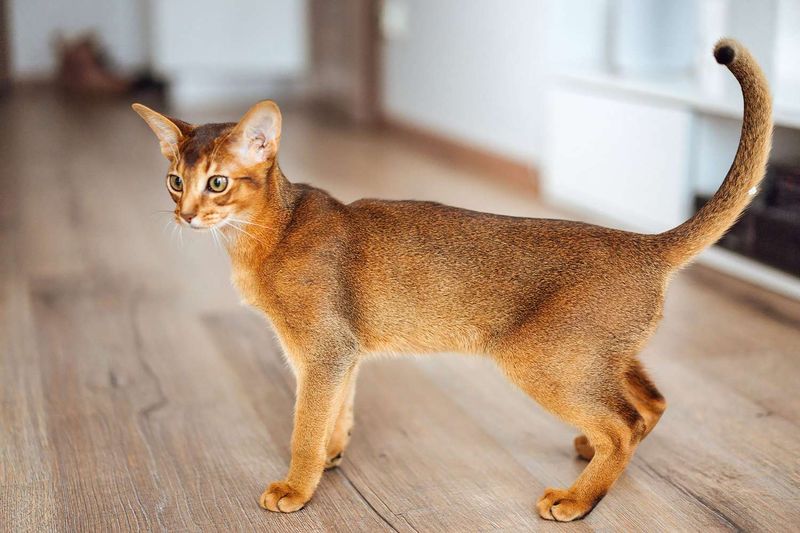
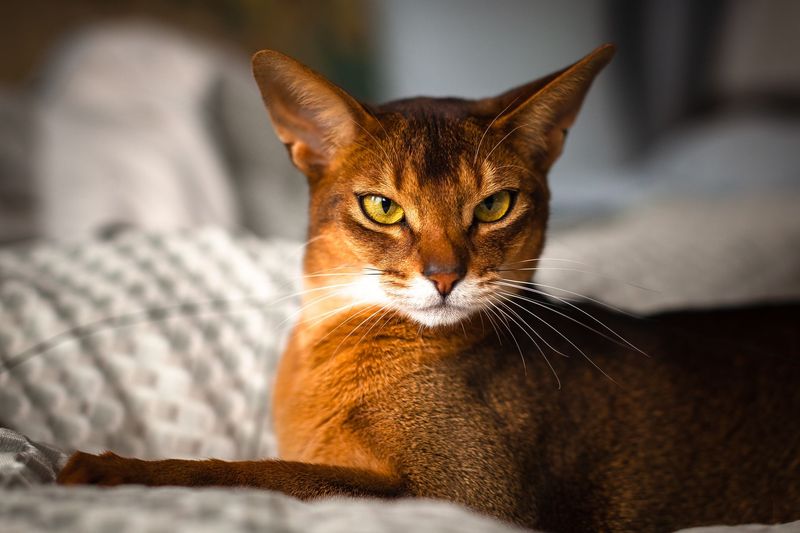
In the world of feline fur, the ticked pattern is a marvel of nature. Found prominently in the Abyssinian breed, this pattern results from the Agouti signaling protein gene mutation. Each hair is adorned with multiple bands of color, creating a shimmering effect. This unique feature adds an exotic touch to these graceful cats.
5. Embryonic Development
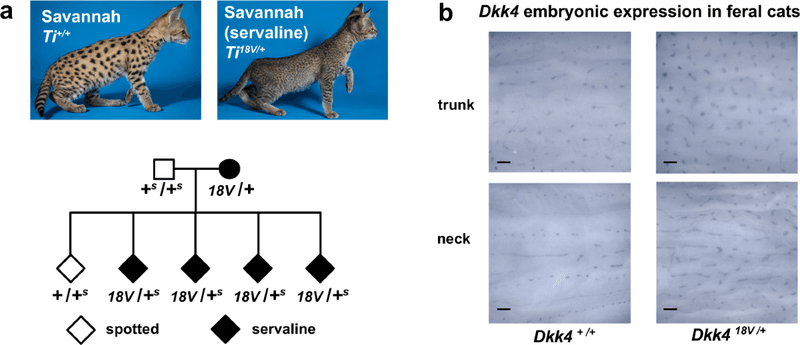
During the delicate stage of embryonic development, genes like DKK4 lay down the blueprint for future fur patterns. These genetic instructions interact with Wnt signaling pathways, orchestrating the intricate designs that later emerge on a cat’s coat. This process is a fascinating dance of biology that shapes feline beauty.
6. Temperature Sensitivity
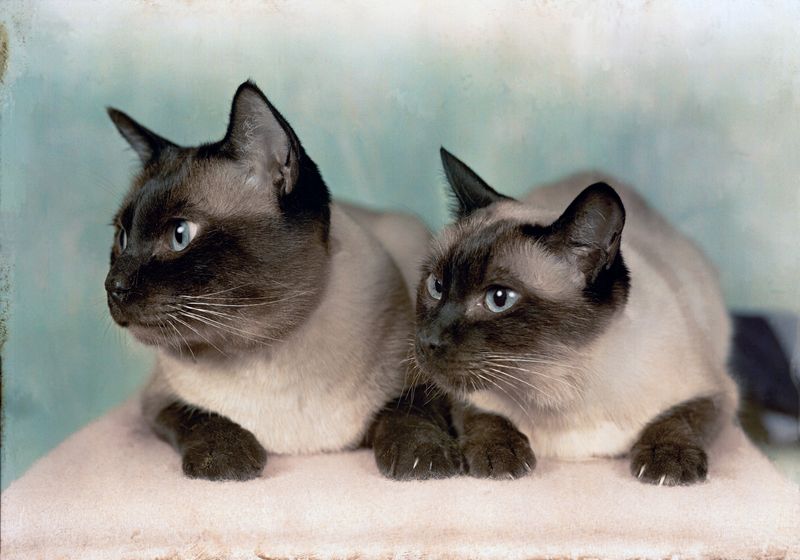
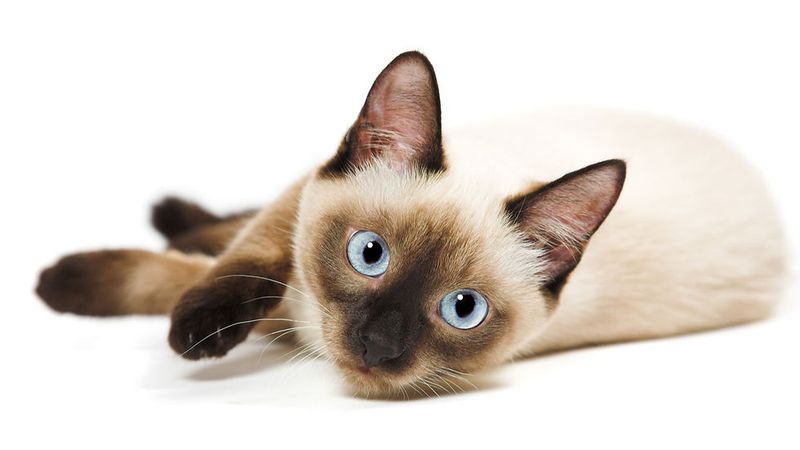
Temperature sensitivity in fur coloration is a genetic wonder. Breeds like Siamese and Himalayan cats exhibit color-point patterns due to a mutation in the tyrosinase enzyme. This enzyme responds to body temperature, creating darker fur on cooler areas. This adaptability showcases nature’s ingenuity in feline evolution.
7. Temperature Effects
Environmental temperature plays a pivotal role in the expression of pigment proteins in some cats. In color-point breeds, cooler body parts develop darker hues due to a temperature-sensitive mutation in the tyrosinase enzyme. This phenomenon exemplifies the intricate relationship between genetics and environment in shaping fur patterns.
8. Wild Ancestors
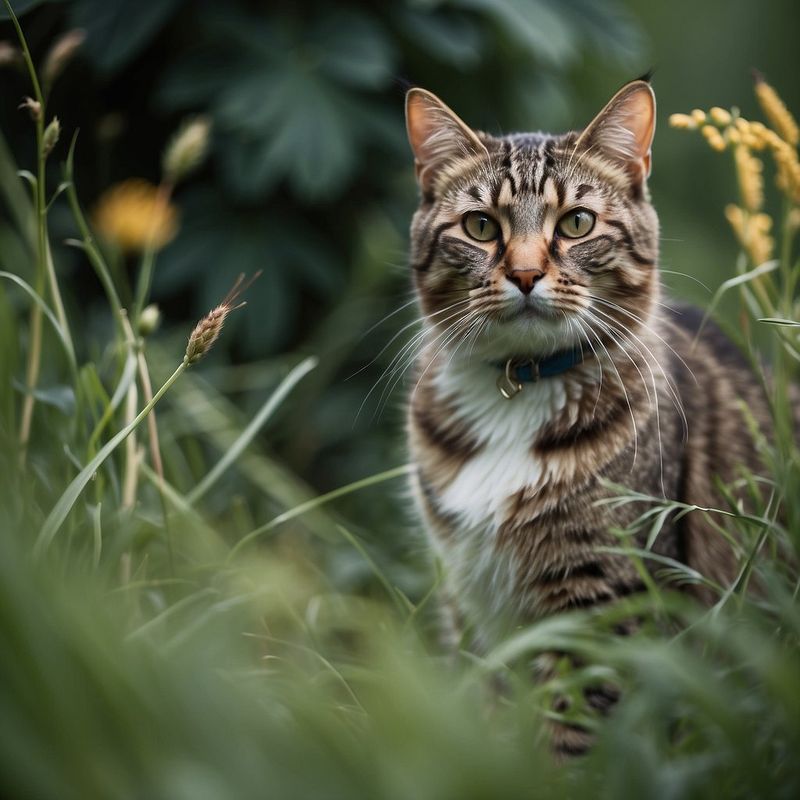
The fur patterns of domestic cats echo those of their wild ancestors, offering insights into their evolutionary past. Camouflage patterns like the mackerel tabby, reminiscent of fish bones, have aided in hunting. These adaptations are vestiges of survival strategies, linking our kitties to the untamed wilderness.
9. Breed Development
Selective breeding has amplified specific fur patterns, such as the Abyssinian’s ticked coat. This process involves choosing cats with desired traits, enhancing their occurrence over generations. The result is a rich tapestry of breeds, each with unique and mesmerizing fur patterns, reflecting human influence on feline genetics.
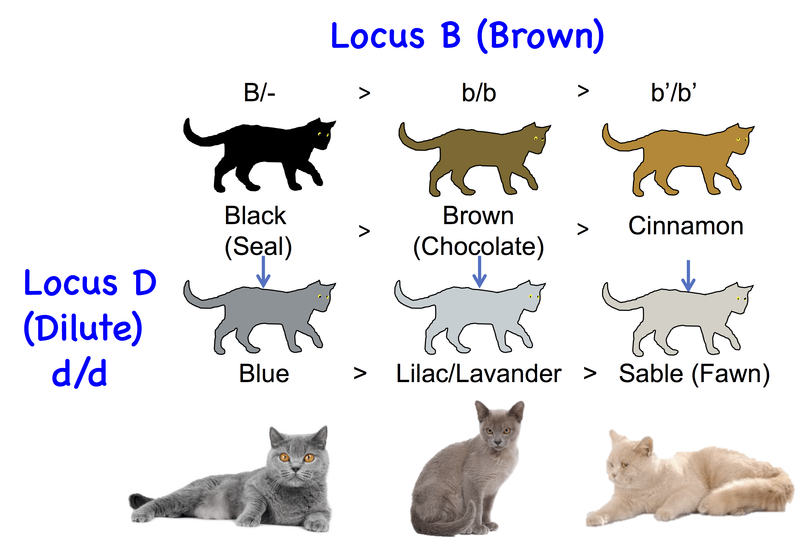
10. Dilute Gene
The Dilute gene acts as a softening brush, transforming intense colors into gentler shades. Black turns to gray, chocolate to lilac, and orange to cream. This genetic alteration enriches the palette of cat fur, giving rise to the pastel hues found in many breeds today. It’s a subtle yet impactful genetic variation.
11. White Spotting
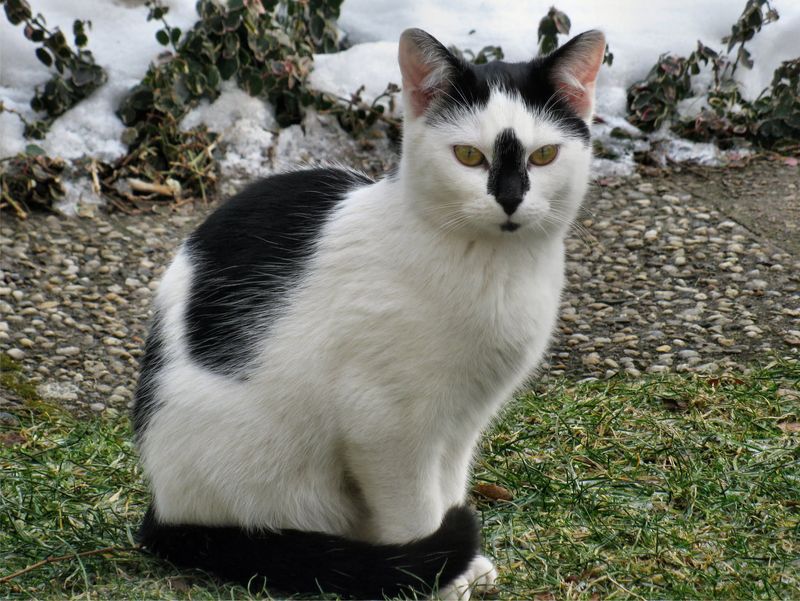
The piebald gene introduces a splash of contrast, creating distinct white patches on a cat’s coat. This genetic trait disrupts pigment cell distribution during development, resulting in bicolor patterns. These striking designs have captured human fascination, leading to iconic appearances in various breeds.
12. Classic Tabby
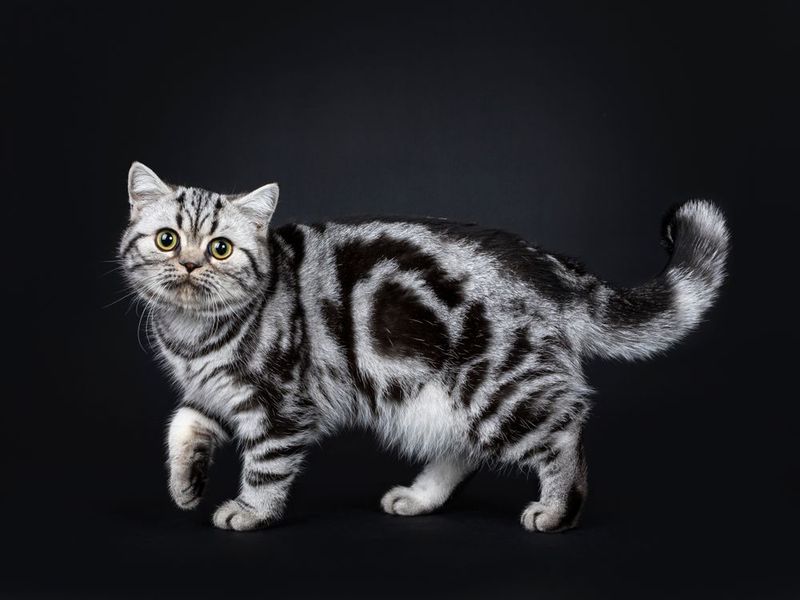
The classic tabby pattern is a masterclass in natural artistry. Defined by wide, rounded spots and the iconic ‘M’ on the forehead, it provides excellent camouflage. This pattern’s beauty lies in its timeless design, echoing the aesthetic preferences of both nature and feline enthusiasts worldwide.
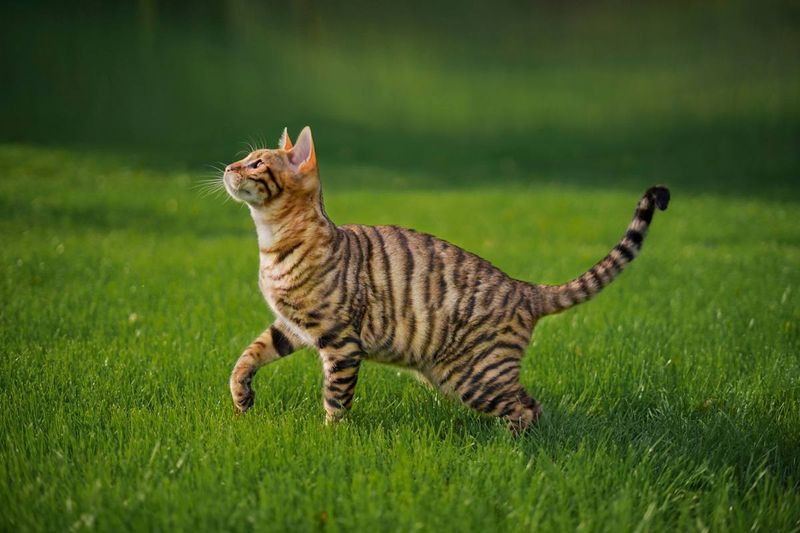
13. Mackerel Tabby
Mackerel tabby cats wear their stripes like a badge of ancestral honor. These thin, parallel lines, reminiscent of fish bones, are thought to aid in stealth and hunting. This pattern speaks volumes about the evolutionary paths our domestic companions have walked, embodying both beauty and functionality.
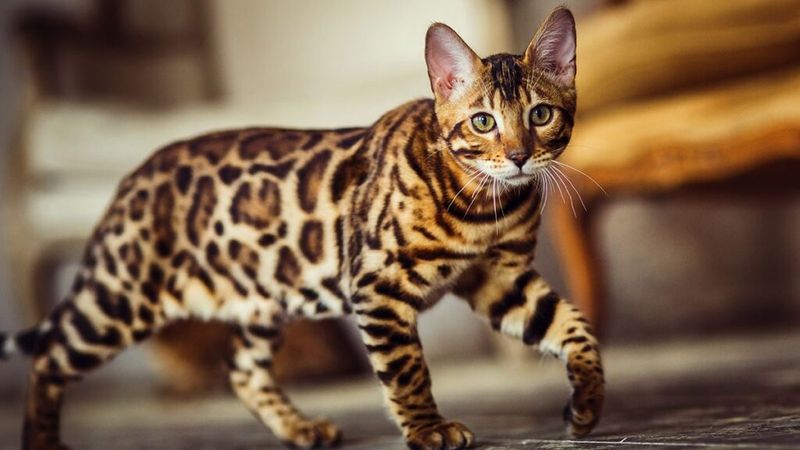
14. Spotted Tabby
The spotted tabby pattern brings a touch of the exotic to domestic breeds. With spots varying from small dots to larger rosettes, this design mimics the wild allure of leopards and ocelots. It’s a testament to the diversity of feline genetics and the surprising twists of nature’s paintbrush.
15. Ticked Tabby
Ticked tabby cats are the epitome of subtlety in fur design. Each hair carries multiple bands of color, resulting in a shimmering, salt-and-pepper effect. This pattern stands out for its understated elegance, an artistic blend of hues that captivates without bold lines or spots.
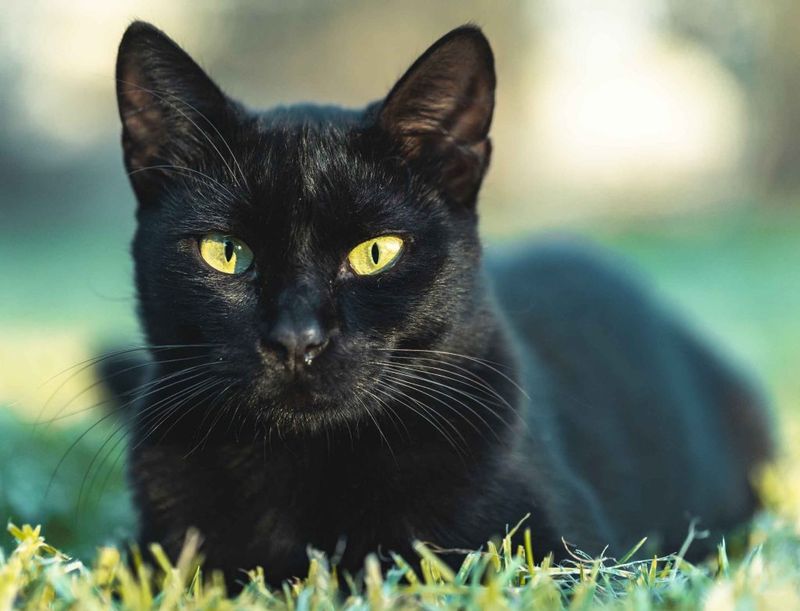
16. Solid or Self-Color
In a world of complexity, solid or self-color cats offer a study in minimalist beauty. Their uniform coats, free of patterns, highlight the pure essence of feline elegance. This simplicity allows their unique personalities to shine through, making them beloved companions around the globe.
17. Bicolor
Bicolor cats bring a splash of variety to the feline color spectrum. With two distinct colors juxtaposed, often white and another hue, they offer a visual delight. This pattern showcases the piebald gene’s artistry, adding diversity and charm to the world of domestic cats.
18. Calico
Calico cats are a patchwork of vibrant colors, combining orange, black, and white in a harmonious display. This pattern is predominantly found in females due to its genetic linkage to the X chromosome. Calico’s kaleidoscope of colors makes it a standout in the feline world, celebrated for its striking appearance.
19. Tortoiseshell
Tortoiseshell cats, often affectionately called ‘torties,’ boast a rich blend of orange and black, sans white. This pattern results from a fascinating mix of genetic factors, producing a mosaic of colors. Known for their feisty personalities, torties add a splash of color and character to any home.
20. Smoke
The smoke pattern is a masterpiece of contrast. With a light undercoat and a darker surface, this pattern creates a mesmerizing shimmering effect. This stunning visual impact, reminiscent of smoke wisping through the air, adds a touch of mystique to the cats that wear it.