📖 Table of Content:
- 1. Dental Issues
- 2. Gastrointestinal Problems
- 3. Respiratory Infections
- 4. Chronic Diseases
- 5. Stress and Anxiety
- 6. Food Preferences
- 7. Food Aversion
- 8. Boredom
- 9. Sensory Decline
- 10. Medications
- 11. Foreign Objects
- 12. Hydration
- 13. Vaccinations and Health
- 14. Social Interaction
- 15. Litter Box Issues
- 16. Weather Changes
- 17. Routine Changes
- 18. Feeding Location
- 19. Food Quality
- 20. Seasonal Allergies
- 21. Neophobia
- 22. Parasites
Is your cat suddenly turning up their nose at mealtime? Loss of appetite in cats can be worrying, but it’s not always a reason to panic. In this comprehensive guide, we explore 22 common reasons why your cat may be refusing food—from stress and dental pain to illness, environmental changes, or even boredom with their current diet.
More importantly, we offer practical, vet-informed solutions to help you identify the cause and respond appropriately. You’ll learn when it’s safe to troubleshoot at home, when it’s time to visit the vet, and how to gently encourage healthy eating habits with tips that work for picky eaters and anxious cats alike.
Whether you’re a new pet parent or a seasoned cat lover, this guide will give you the knowledge and confidence to support your feline through feeding challenges and get them back to their happy, hungry self.
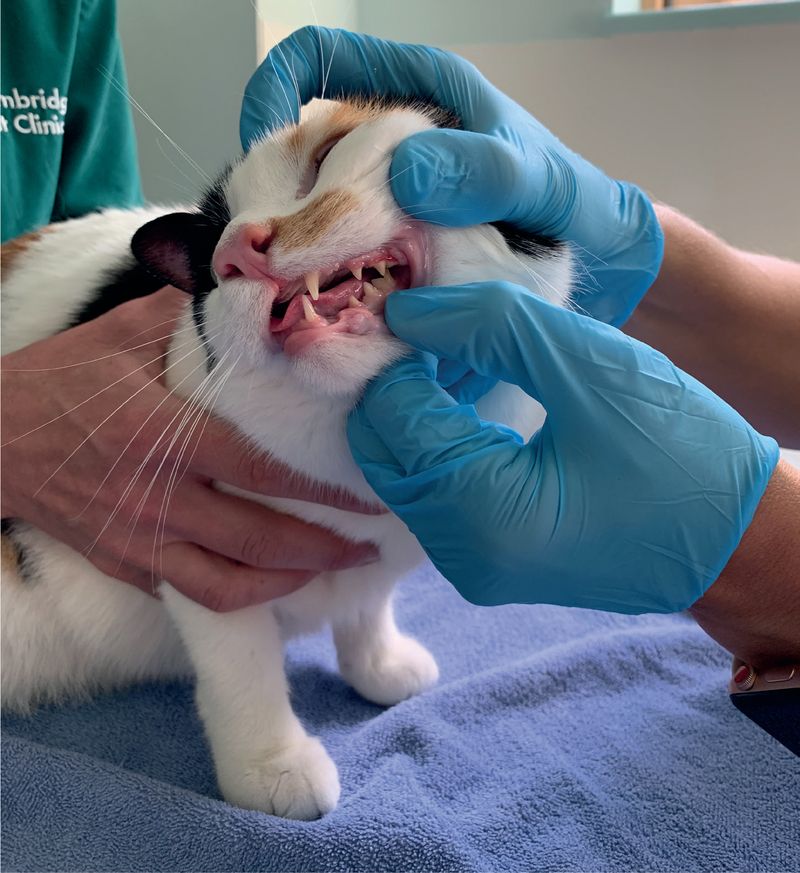
1. Dental Issues
Cats with dental issues like gum disease or toothaches often find eating painful. Symptoms such as drooling, bad breath, and difficulty chewing may indicate a problem. It’s essential to schedule a veterinary dental examination to identify and treat any underlying dental problems. Addressing these issues can help restore your cat’s appetite and overall health. Cats may shy away from food, preferring to avoid the discomfort caused by eating. Ensuring proper dental care can significantly improve their quality of life. Regular check-ups can prevent these issues from affecting your feline friend.
2. Gastrointestinal Problems
Gastrointestinal issues like pancreatitis or inflammatory bowel disease can lead to nausea and discomfort, making food unappealing. Cats experiencing these issues might show signs of lethargy and weight loss. Consulting a veterinarian for appropriate diagnostics and treatment plans is crucial. These conditions can seriously affect your cat’s health and happiness if left untreated. Monitoring your cat’s eating habits and seeking timely medical attention can make a significant difference. Proper treatment can help restore their appetite and vitality, ensuring they remain healthy and active.
3. Respiratory Infections
Cats with upper respiratory infections often lose their sense of smell, which can make food seem less appealing. Providing warm, aromatic foods can entice your cat to eat. Veterinary care is essential if symptoms persist. These infections can cause sneezing, runny nose, and watery eyes, making your cat feel miserable. Prompt treatment can prevent the infection from worsening and help restore your cat’s appetite. Keeping your cat comfortable and hydrated during recovery is vital. Regular vaccinations can help prevent these infections from occurring.
4. Chronic Diseases
Chronic conditions like kidney disease, diabetes, or hyperthyroidism can severely impact a cat’s appetite. Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for managing these health issues. Symptoms might include increased thirst, weight loss, or lethargy. Addressing these conditions with proper treatment can improve your cat’s quality of life. Monitoring their behavior and dietary habits helps in early detection and intervention. Ensuring your cat receives appropriate care and medication can make a significant difference. Managing chronic diseases requires dedication but can lead to a happier, healthier cat.
5. Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can significantly affect a cat’s eating habits. Changes like new pets, moving, or loud noises may lead to reduced food intake. Maintaining a consistent routine and providing a quiet, safe feeding environment can alleviate stress. Cats are creatures of habit, and sudden changes can disrupt their appetite. Offering a calm and stable environment helps them feel secure, encouraging normal eating behavior. Recognizing signs of anxiety early can help prevent long-term issues. Comfort and consistency are key in helping your cat overcome stress-related eating problems.
6. Food Preferences
Cats can be particular about their food flavors, textures, or temperatures. Experimenting with different types of food can help find what appeals to your cat. Warming food slightly or adding flavorful toppings may entice them to eat. Cats’ preferences can change over time, requiring adjustments in their diet. Awareness of their likes and dislikes ensures they receive adequate nutrition. Introducing new foods gradually can prevent food aversions. Understanding your cat’s unique taste can lead to more satisfying meals and a happier pet.
7. Food Aversion
Cats may develop food aversions if they associate a particular food with illness. Gradually introducing new foods can help in overcoming this issue. Avoiding force-feeding prevents negative associations with mealtime. Observing your cat’s reactions to different foods is essential in managing aversion. Patience and persistence are key in finding suitable dietary options. Understanding their aversions helps in creating a positive eating experience. Providing a variety of options ensures they receive balanced nutrition while respecting their preferences.
8. Boredom
Monotony in meals can make eating unappealing for cats. Rotating different food types and flavors keeps your cat interested in mealtime. Offering variety can prevent boredom and ensure they receive a balanced diet. Cats, like humans, appreciate novelty in their meals. Exploring new tastes and textures can reignite their interest in food. Ensuring diverse meal options can improve their eating habits and overall health. Observing your cat’s preferences helps tailor their diet to their liking, making mealtime enjoyable again.
9. Sensory Decline
As cats age, their senses of taste and smell may diminish, affecting their interest in food. Offering more aromatic and flavorful foods can stimulate their appetite. Ensuring easy access to meals supports their dietary needs. Observing changes in behavior helps in adjusting their diet accordingly. Catering to their sensory changes can improve their quality of life. Providing enticing meals encourages regular eating habits, promoting health and well-being. Understanding the needs of senior cats ensures they enjoy their golden years with comfort and satisfaction.
10. Medications
Some medications can suppress a cat’s appetite, impacting their willingness to eat. Discussing with your veterinarian the possibility of adjusting medications or their administration times can help. Monitoring their eating habits is crucial in managing side effects. Understanding the impact of medications on appetite helps in ensuring proper nutrition. Working closely with your vet can lead to effective solutions. Addressing these issues promptly can restore normal eating patterns, improving your cat’s health. Managing medication-related appetite changes requires patience and attention to detail.
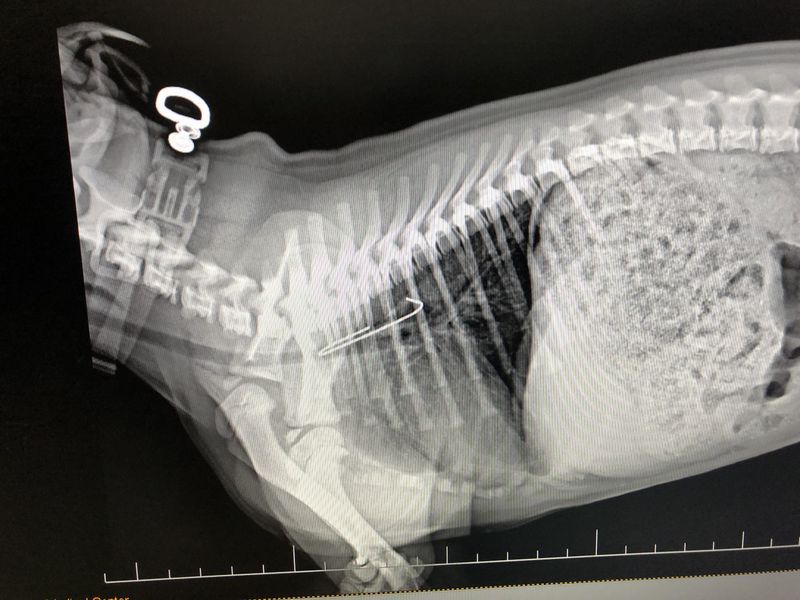
11. Foreign Objects
Ingesting non-food items can cause discomfort and lead to food refusal in cats. Ensuring your cat’s environment is free from small objects that could be ingested is crucial. Observing your cat’s behavior can help in preventing such incidents. Creating a safe and hazard-free environment supports their well-being. Prompt medical attention is necessary if ingestion is suspected. Prevention is key in avoiding complications arising from foreign objects. Ensuring a secure living space allows your cat to explore safely, reducing risks associated with ingestion.
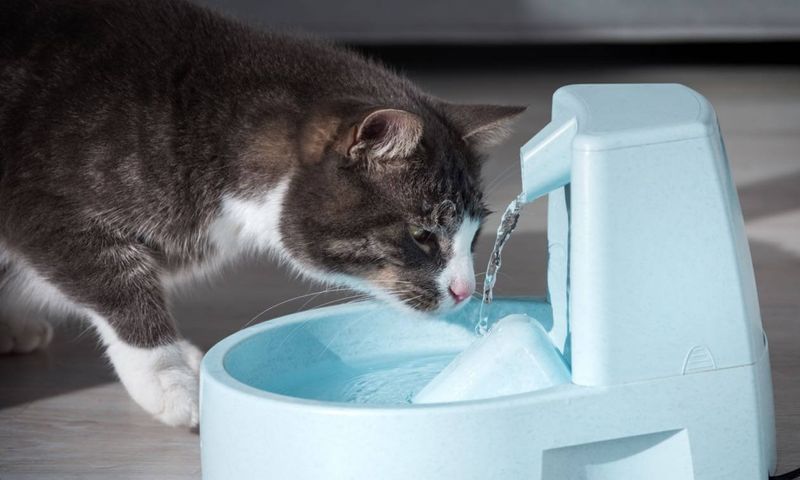
12. Hydration
Dehydration can lead to reduced appetite in cats. Ensuring they have access to fresh water at all times is essential. Cats may be reluctant to eat if they are not properly hydrated. Providing wet food can also help maintain hydration levels. Monitoring their water intake helps in preventing dehydration-related appetite loss. Encouraging regular drinking habits supports their overall health. Understanding the importance of hydration ensures your cat remains active and interested in food. A well-hydrated cat is more likely to enjoy their meals.
13. Vaccinations and Health
Regular vaccinations play a vital role in maintaining a cat’s health and appetite. Keeping up with vaccination schedules can prevent illnesses that affect eating habits. A healthy cat is more likely to have a strong appetite. Consulting with your veterinarian ensures they receive necessary vaccines on time. Understanding the importance of vaccinations supports long-term health and vigor. Protecting against common diseases improves their quality of life. Staying informed about your cat’s health needs helps maintain their appetite and enthusiasm for food.
14. Social Interaction
Social interactions can influence a cat’s willingness to eat. Engaging with your cat during mealtime can encourage eating. Creating a positive and interactive feeding environment enhances their appetite. Cats are social creatures and may enjoy companionship during meals. Understanding their social needs supports better eating habits. Observing their behavior during feeding times helps tailor interactions to suit their preferences. Fostering a bond through shared mealtimes strengthens the relationship and promotes regular eating patterns.
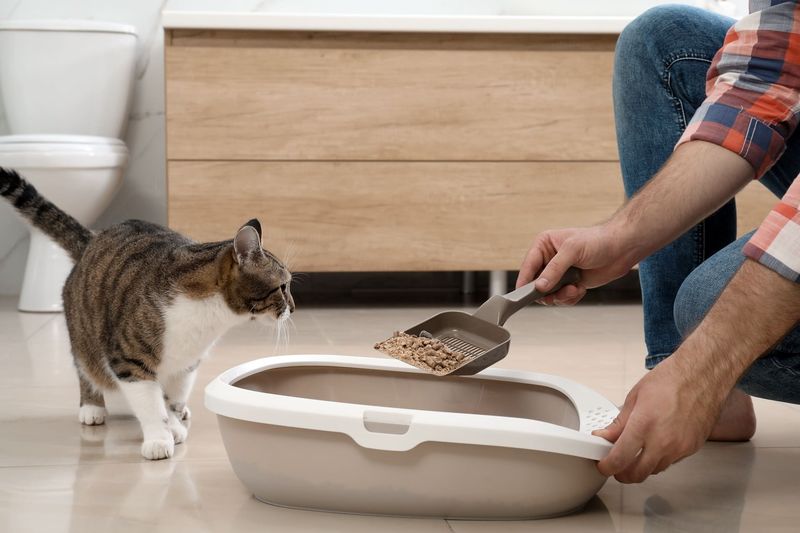
15. Litter Box Issues
Litter box issues can lead to stress and decreased appetite in cats. Maintaining a clean and accessible litter box can alleviate these problems. Cats prefer a tidy environment and may refuse food if their litter box is unclean. Ensuring regular cleaning and proper placement supports their comfort. Observing any sudden changes in behavior can help identify litter box-related stress. Understanding the importance of hygiene in their daily routine improves their overall well-being. A clean environment encourages healthy eating habits.
16. Weather Changes
Weather changes, like cold or rainy days, can affect a cat’s mood and appetite. Providing warm, cozy environments can make mealtime more appealing during such times. Cats may be less active in adverse weather, impacting their eating habits. Ensuring a comfortable living space supports their well-being. Observing their behavior during different weather conditions helps in adjusting their diet accordingly. Understanding the link between weather and mood ensures they remain interested in food regardless of the climate. Comfort is key in encouraging consistent eating patterns.
17. Routine Changes
Changes in routine, such as travel or new schedules, can disrupt a cat’s eating habits. Maintaining consistency in feeding times and environments helps mitigate these effects. Cats thrive on routine, and sudden changes may lead to food refusal. Preparing for changes by gradually adjusting schedules ensures smoother transitions. Observing their behavior helps in recognizing stress related to routine disruptions. Understanding the importance of stability in their daily lives improves their overall well-being. Consistency in care encourages regular eating habits and a happy cat.
18. Feeding Location
The location of a cat’s feeding area can influence their eating behavior. Choosing a quiet, safe spot encourages regular meals. Cats may refuse food if they feel threatened or uncomfortable. Ensuring a peaceful environment supports their dietary habits. Observing their preferences helps in selecting the ideal feeding location. Understanding their need for a secure space improves mealtime experiences. Providing a designated area free from disturbances fosters regular eating patterns. Comfort and safety are key in maintaining their interest in food.
19. Food Quality
The quality of food plays a significant role in a cat’s willingness to eat. Offering high-quality, nutritious options ensures they receive essential nutrients. Cats may refuse low-quality food, impacting their health. Providing balanced meals supports their overall well-being. Observing their reactions to different foods helps identify preferences. Understanding the importance of nutrition encourages better eating habits. Investing in quality food ensures they remain healthy and active. A proper diet is crucial for maintaining their interest in meals.
20. Seasonal Allergies
Seasonal allergies can impact a cat’s comfort and eating habits. Symptoms like itching or sneezing may lead to food refusal. Addressing allergies with appropriate treatments can improve their appetite. Understanding the seasonal nature of allergies helps in managing symptoms effectively. Observing changes in behavior during allergy seasons aids in early detection. Providing relief through medication or environmental adjustments supports their well-being. Ensuring a healthy living space minimizes discomfort and encourages normal eating patterns.
21. Neophobia
Neophobia, or fear of new things, can cause cats to refuse unfamiliar foods. Gradually introducing new items can help overcome this fear. Cats are creatures of habit and may resist changes in their diet. Creating a supportive environment encourages exploration of new foods. Observing their reactions aids in understanding their comfort levels. Understanding the nature of neophobia helps in managing dietary changes. Patience and consistency are key in helping them adapt to new eating experiences, promoting a diverse and balanced diet.
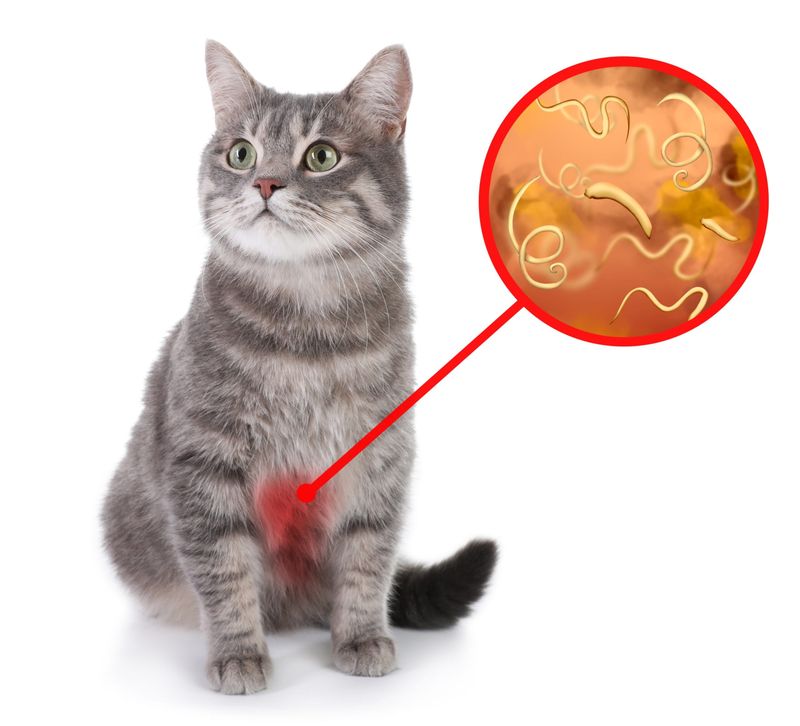
22. Parasites
Parasites can cause discomfort and reduce a cat’s appetite. Regular veterinary check-ups and proper treatments are essential for preventing infestations. Observing signs like weight loss or lethargy helps in early detection. Understanding the impact of parasites on health ensures timely interventions. Providing a clean environment reduces risks associated with infestations. Ensuring regular deworming and parasite control supports their overall well-being. Addressing these issues promptly can restore normal eating patterns, promoting health and vitality in your feline companion.